It's no secret that ADHD comes with its fair share of struggles. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder can look like issues with focus and prioritizing tasks or difficulties with impulse control.
ADHD medication can alleviate some of the symptoms associated with ADHD. Though it's not a cure-all, many use it with other tools to create a multimodal approach to ADHD treatment. With so many medication options, it can feel overwhelming when you begin this journey.
This article clarifies the differences between two well-known ADHD drugs, Adderall and Vyvanse (aka Elvanse in Europe).
Too long; didn't read
- Adderall and Vyvanse are amphetamine-based psychostimulants.
- They both increase chemicals in the brain that help reduce ADHD symptoms.
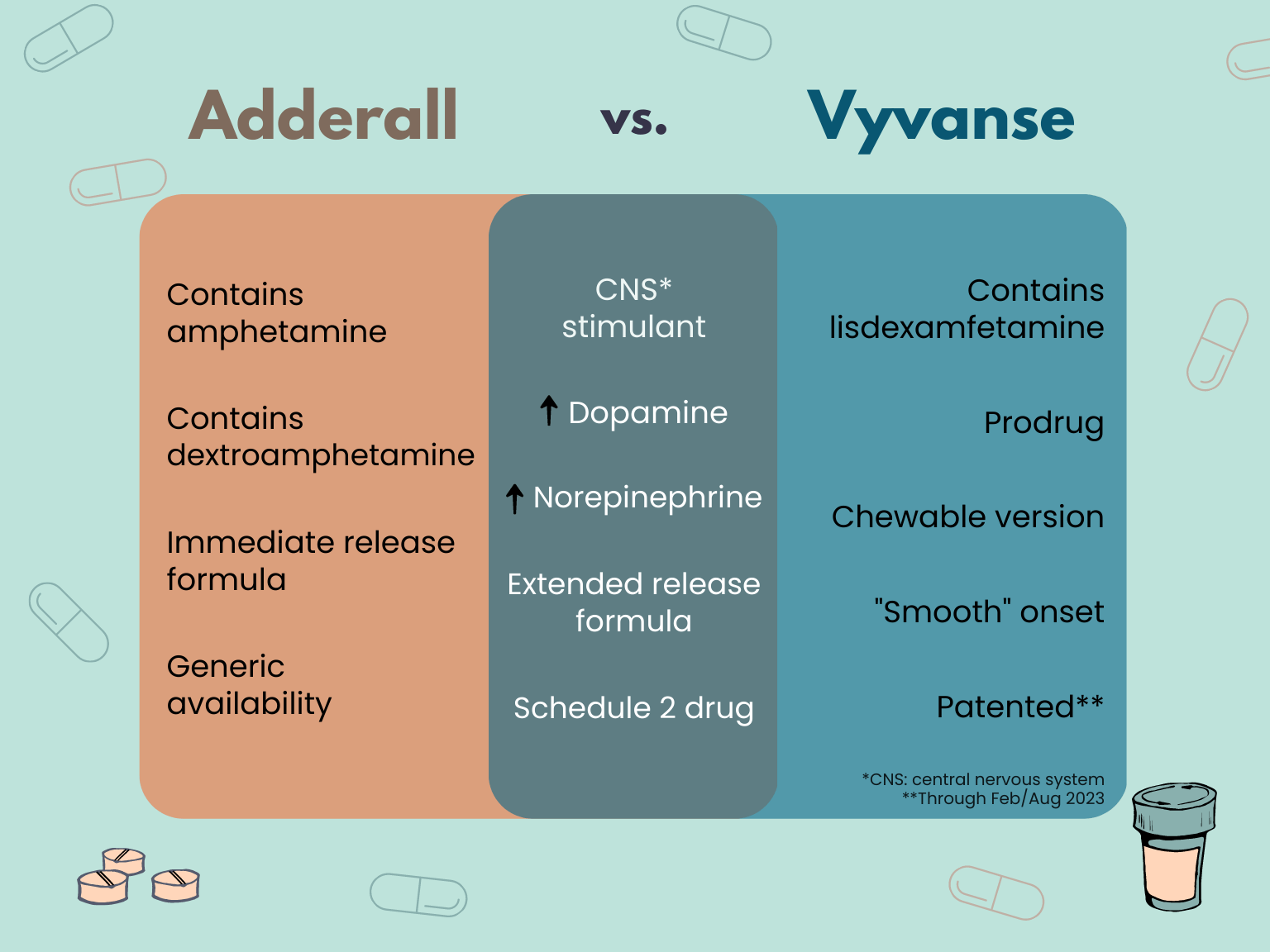
- Adderall is a mix of dextroamphetamine and amphetamine, whereas Vyvanse contains lisdexamfetamine.
- Vyvanse is a prodrug, meaning it contains an inactive drug that the body must convert into an active drug. (This is why Vyvanse has a slower onset—and longer duration—than Adderall.)
- Adderall is available in immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR;ER) formulas, while Vyvanse is always extended-release (due to it being a prodrug.)
- The side effects of both medications are very similar.
- Both Adderall and Vyvanse have shown success in helping ADHDers, and the best option varies from person to person.
Key similarities between Adderall and Vyvanse
The main similarity between these two ADHD medications is that they are both:
- (Psycho)stimulants
- Amphetamine-based
- Schedule II drugs (they have a high potential for abuse or dependency)
As stimulants, both of these medications increase neurotransmitters in the brain that help to improve focus, calm hyperactive symptoms, and reduce impulsivity. The primary neurotransmitters affected by stimulants are dopamine and norepinephrine (aka noradrenaline), which are integral to brain function.1
What are the main differences between Adderall and Vyvanse?
Often, people think that Adderall and Vyvanse are the same, and though they share similarities, they have important differences.
Different active ingredients
The active ingredients in Adderall are dextroamphetamine (D-amphetamine) and amphetamine, which increases dopamine and norepinephrine while blocking norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake.
Vyvanse contains lisdexamfetamine, a prodrug, which first has to be metabolized by the liver and converted into dextroamphetamine before the body can use it. Eventually, Vyvanse leads to an increase in dopamine and norepinephrine in the prefrontal cortex.2,3
How they're metabolized
The most notable difference between Adderall and Vyvanse is they're metabolized.
Vyvanse is a prodrug, meaning the ingredient is an inactive drug that must go through a metabolic process in the body that chemically converts it into an active drug. This is why Vyvanse takes longer to start working and doesn't have such an intense "kickstart."
Adderall is not a prodrug, so it starts working much quicker, but only last a few hours. Some may prefer Adderall's rapid onset, as it may help them become more aware of when it "kicks in." On the other hand, some people find it jarring to their system, which is why they would likely opt for Vyvanse.
Release time: extended and immediate
Adderall is available in both immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR or ER) formulas. Vyvanse, by nature, is always an extended-release form since it's a prodrug.
The immediate-release Adderall is fast-acting but doesn't last as long. You can expect this form of Adderall to last around 3-4 hours, per the FDA. Because the IR (immediate release) version only lasts for a short time, many people take multiple doses throughout the day.
Adderall's extended-release option (Adderall XR) can last around 8-12 hours, so you typically only need one daily dose.
Vyvanse can take 1-2 hours to take effect but can last 12-14 hours and typically only requires one daily dose.
Dosage differences
ℹ️ For your reference: the abbreviation mg is used to represent the measurement of milligrams.
Adderall doses
Immediate release
- 5 mg
- 7.5 mg
- 10 mg
- 12.5 mg
- 15 mg
- 20 mg
- 30 mg
The standard starting dose for Adderall is 5 mg, once or twice a day. From there, the prescribing doctor can help patients find the right dosage.
Extended release
- 5 mg
- 10 mg
- 15 mg
- 20 mg
- 25 mg
- 30 mg
The standard dose for Adderall XR is 10-20 mg per morning, with a maximum dose of 40 mg per day.
Vyvanse doses
Vyvanse comes in a chewable form or a capsule form. Both Vyvanse variations are available in the following doses:
- 10 mg
- 20 mg
- 30 mg
- 40 mg
- 50 mg
- 60 mg
- 70 mg (only capsules)
The standard starting dose for adults is 30 mg once a day and then increased by 10 - 20 mg per week as needed without exceeding the daily 70 mg maximum.
What are the side effects of Adderall and Vyvanse?
Adderall and Vyvanse have similar side effects. However, since Vyvanse is a prodrug, the side effects may not be as intense as those from Adderall.4
However, both medications can cause any of the following:
Common side effects of Adderall and Vyvanse:
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Mood changes
- Nausea
- Tics or body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs)
- Trouble sleeping
Rare side effects:
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Increased body odor and sweating
- Muscle weakness
- Severe anxiety
- Severe weight loss
⚠️ Please note that these lists are not exhaustive, and other side effects are possible. Speak with your prescribing doctor if you have questions or concerns.
Which drug is best for ADHD?
Because bodies are different, it's impossible to say whether Adderall or Vyvanse is better for you. One person may swear by Adderall, while the next person finds that Adderall gives them issues that Vyvanse does not, or vice versa.
Both are effective in treating ADHD; ultimately, the decision comes down to the conversation you have with your doctor regarding the risks and benefits of each medication.
Look into pharmacogenetics testing
Pharmacogenetics testing is a type of genetic testing that would look at your genetic makeup to determine how you might respond to certain medications. A DNA analysis would identify gene variations that affect how your body processes and metabolizes drugs. Once the results are in, your healthcare provider can help you choose the medication that's most likely to be effective and safe for your body.
Learn more about pharmacogenetics here.
-
Sources
1 Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | The Pharmacology of Amphetamine and Methylphenidate: Relevance to the Neurobiology of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Other Psychiatric Comorbidities
2 CNS Spectrums | Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate: A Prodrug Stimulant for the Treatment of ADHD in Children and Adults
3 Biomolecules and Therapeutics | Potential for Dependence on Lisdexamfetamine - In vivo and In vitro Aspects
4 Future Medicinal Chemistry | Cytochrome P450-activated prodrugs